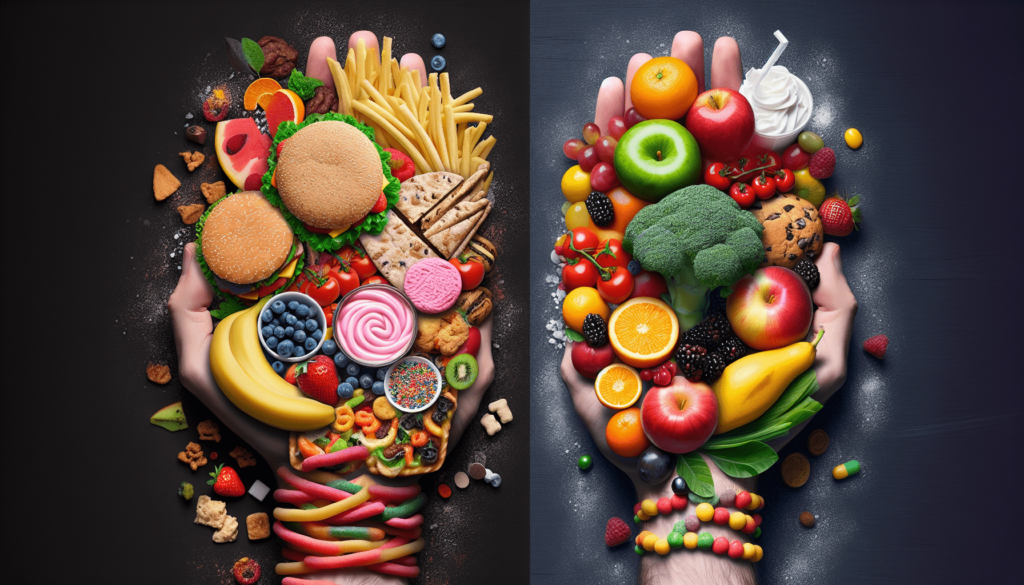
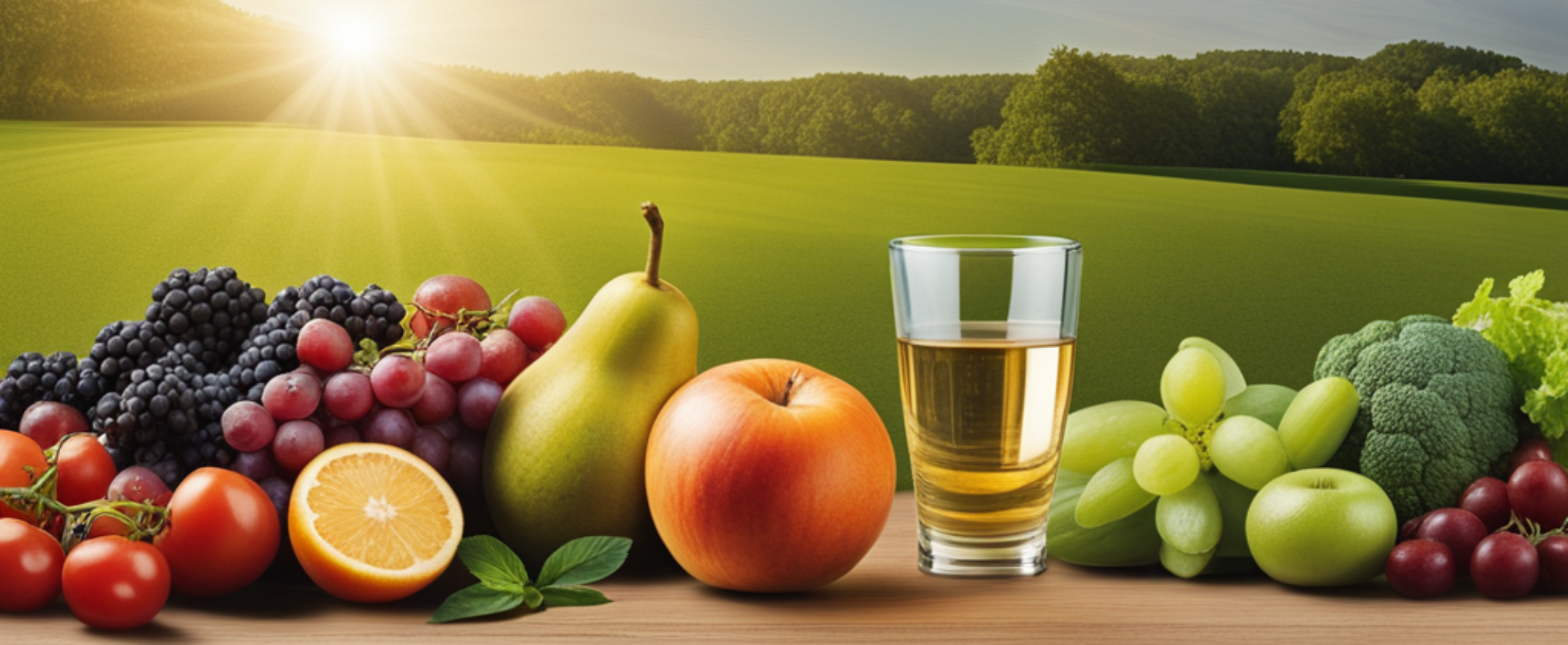
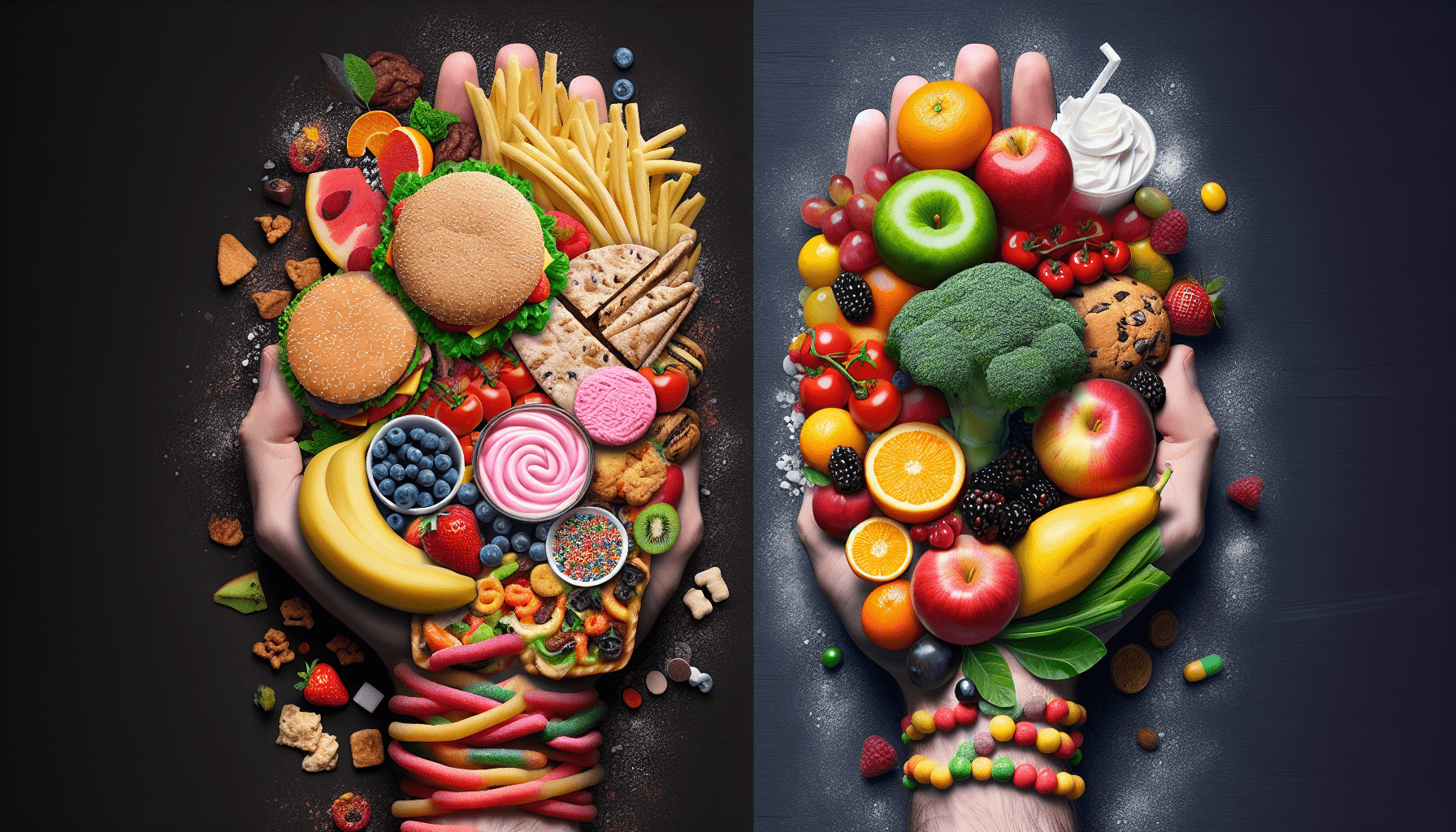In today’s fast-paced world, where fad diets and conflicting nutritional advice abound, it’s easy to get caught up in the buzzwords of diet and nutrition. However, understanding the fundamental difference between the two is vital for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. While diet refers to the specific food and drink choices you make, nutrition goes deeper, encompassing the way your body processes, absorbs, and utilizes those nutrients. By grasping this distinction, you’ll be empowered to make more informed decisions about your health and wellbeing.
Definition of Diet and Nutrition
What is diet?
Diet refers to the specific food and drink choices that you regularly consume. It is the sum of all the foods and beverages that make up your daily eating pattern.
What is nutrition?
Nutrition, on the other hand, is the science of how the body utilizes the nutrients in the foods and drinks we consume to support growth, repair, and overall health.
Focus and Purpose
Diet: Focus on weight management
When it comes to diet, the main focus is often placed on weight management. Many people follow specific diets in order to lose weight, maintain a certain weight, or even gain weight.
Nutrition: Focus on overall health and well-being
On the other hand, nutrition has a broader focus on overall health and well-being. While weight management may be a part of it, nutrition emphasizes providing the body with the essential nutrients it needs to function optimally.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Components
Diet: Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the major components of our diet and provide the body with energy. They include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. When following a specific diet, people often pay attention to the macronutrient composition of their meals.
Diet: Micronutrients
Micronutrients are essential vitamins and minerals that our bodies need in smaller amounts. While they don’t provide energy, they play crucial roles in supporting various body functions. However, some diets may overlook the importance of these micronutrients.
Nutrition: Macronutrients
Just like in a diet, nutrition also considers the macronutrients that provide energy to the body. A balanced nutrition plan ensures that you get an appropriate amount of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats for your overall health and well-being.
Nutrition: Micronutrients
Similarly, nutrition also takes into account the importance of micronutrients. Ensuring that your nutrition plan includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and other nutrient-rich foods will help meet your body’s micronutrient needs.
Food Choices
Diet: Restrictive approach
Many diets take a restrictive approach, focusing on certain food groups or specific types of food. This can often lead to limited food choices and even strict rules about what you can and cannot eat.
Diet: Emphasis on specific foods or food groups
Some diets emphasize the consumption of specific foods or food groups. For example, a low-carb diet may recommend cutting out or greatly reducing carbohydrates, while a vegan diet eliminates all animal products.
Nutrition: Balanced approach
The concept of nutrition promotes a balanced approach to food choices. Rather than excluding entire food groups, it encourages a variety of foods from different groups to ensure a well-rounded intake of nutrients.
Nutrition: Emphasis on variety and whole foods
In nutrition, there is a strong emphasis on incorporating a wide variety of whole foods into your diet. Whole foods are those that are minimally processed and retain their natural nutrients.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Long-term Impact
Diet: Short-term results, potential for yo-yo effect
Many diets are designed to produce quick results in terms of weight loss or other specific goals. However, the focus on short-term results can lead to a “yo-yo” effect where weight is lost and regained repeatedly over time.
Nutrition: Long-term sustainable habits
In contrast, nutrition aims to establish long-term habits that can be sustained over a lifetime. It encourages the adoption of healthy eating patterns that support overall health and well-being, rather than focusing solely on short-term outcomes.
Health Benefits
Diet: Weight loss, specific conditions (if tailored)
Diets are often associated with weight loss, and some may be tailored to address specific health conditions. For example, a doctor may prescribe a low-sodium diet for individuals with high blood pressure or a gluten-free diet for those with celiac disease.
Nutrition: Improved overall health, disease prevention
Nutrition, with its holistic approach, offers a range of health benefits. It supports overall well-being, improves bodily functions, and helps prevent various diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Nutritional Needs
Diet: May neglect certain nutritional needs
While following a specific diet, there is a possibility of neglecting certain nutritional needs. For instance, a restrictive diet may not provide enough essential vitamins and minerals if not carefully planned.
Nutrition: Aims to fulfill all nutritional needs
Nutrition, being rooted in the science of nourishment, aims to meet all of your nutritional needs. It considers the recommended daily intake of various vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients to support optimal health.
Mindset and Behavior
Diet: May lead to food anxiety or guilt
Some diets can create a negative mindset around food, leading to feelings of anxiety or guilt when deviating from the strict rules and restrictions. This can negatively impact the individual’s relationship with food.
Nutrition: Encourages a positive relationship with food
On the other hand, nutrition promotes a positive and balanced relationship with food. It emphasizes enjoying a variety of foods in moderation, without labeling foods as “good” or “bad.”
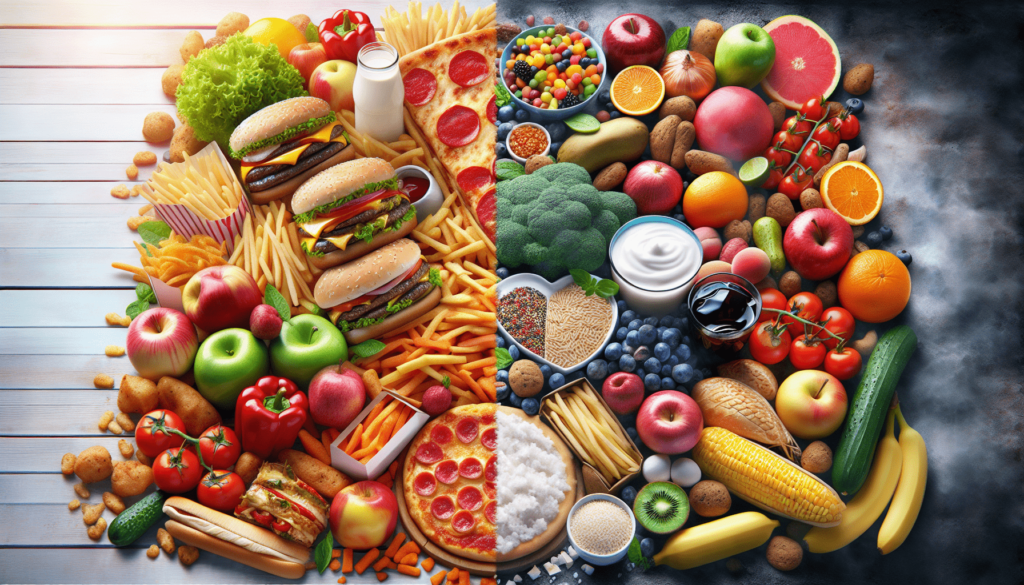

Professional Guidance
Diet: Often self-prescribed or fad-based
Many people adopt diets on their own or based on popular trends without seeking professional guidance. This can lead to following fad diets that are not backed by scientific evidence, potentially harming health in the long run.
Nutrition: Recommendations by qualified nutritionists/dieticians
To ensure optimal nutrition, it is advisable to seek guidance from qualified nutritionists or dieticians who can tailor a nutrition plan based on your individual needs, goals, and any specific health conditions.
Sustainable Lifestyle
Diet: Often seen as temporary
Diets are often seen as short-term endeavors to achieve a specific goal, such as losing weight for an event or fitting into a certain dress size. This mindset may not lead to long-term success or sustainable lifestyle changes.
Nutrition: Focuses on long-term, sustainable lifestyle changes
In contrast, nutrition focuses on long-term, sustainable lifestyle changes. It encourages gradual modifications to your eating patterns, allowing you to establish healthy habits that can be maintained throughout your life.
In conclusion, while diet and nutrition are related, they have distinct differences in their focus, purpose, and approach. While diets may offer short-term results, they often neglect certain nutritional needs and can create negative mindsets around food. On the other hand, nutrition prioritizes overall health, encourages a positive relationship with food, and aims to fulfill all nutritional needs. By prioritizing nutrition, seeking professional guidance, and embracing a balanced and sustainable approach, you can pave the way for a healthier and happier life.